Dive into the core of crypto: What is hashing in cryptocurrency? It’s the locked vault where digital coins are safe. This is no dull math lesson! Get ready to grasp how secure codes keep your virtual cash sound. Hang tight, as I shed light on the vital cog in the crypto machine.
Understanding the Essence of Hashing in Cryptocurrency
Decoding Hash Functions and Their Role in Blockchain
Think of blockchain as a digital ledger. A ledger that everyone can see. It’s a chain of blocks, and each one holds a ton of transactions. But how do we keep it all safe? That’s where hashing comes in.
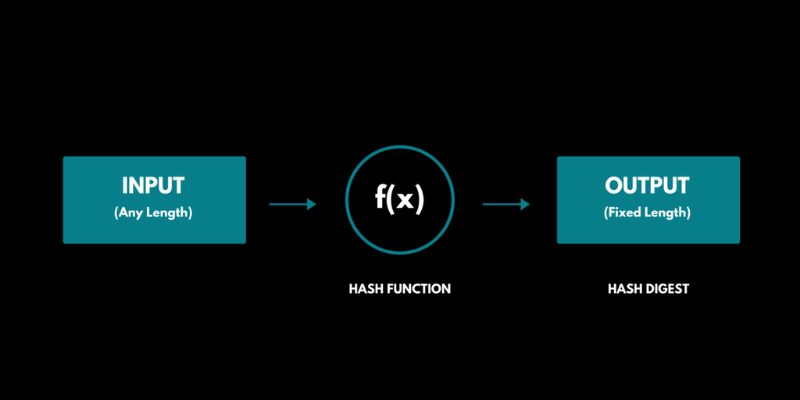
Hashing takes data and scrambles it up. Imagine mixing up a jigsaw puzzle and putting it in a box. What comes out, the ‘hash value’, is unique. Like a fingerprint, no two are the same. If you change even just one letter of the original data, a whole new hash is made.
These scrambled puzzles work because they’re hard to solve. But once we have the solution, it’s easy to check. This way, everyone knows the data hasn’t changed. So, in blockchain, hashing keeps our data safe. It’s like a seal on those old letters, unbroken until it reaches the right person.
In cryptocurrencies, each transaction is hashed. Many hashes come together to form a ‘Merkle tree’. It’s a tree because it starts with lots of little bits, which are hashed together to make bigger bits. Until we’re left with one big ‘root’ hash.
Everyone on the network has the same Merkle tree. That means nobody can cheat. If they try, their tree will be different. It just won’t match the rest.
The Importance of SHA-256 and Its Impact on Bitcoin
Now, let’s talk about SHA-256. This stands for Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit. It is the brain behind the security of Bitcoin.
SHA-256 is a recipe for making a hash. We put our data in, follow the steps, and get a hash out. This recipe makes it super tough to guess the original data from the hash. It also keeps it safe from collisions. That means you won’t make the same hash from different data.
Bitcoin uses SHA-256 to keep track of all the coin moves. Every time someone sends or gets Bitcoin, SHA-256 is on the job. It makes sure the transaction is real and not messed with.
When miners try to add new blocks to the chain, SHA-256 comes into play. They have to find a special number, a ‘nonce’, that gives the right hash. It’s like a winning lottery ticket. When they find it, they add the block and get some Bitcoin.
Because SHA-256 is complex, it’s super hard to fake. This stops bad folks from messing with Bitcoin. It keeps it safe and sound. So, SHA-256 isn’t just important; it’s the hero keeping Bitcoin alive and kicking.
In all, hashing is the secret sauce in the crypto world. It keeps our digital money safe. It stops cheaters. And it helps good transactions keep on rolling. All without letting anyone see the details inside. Isn’t that amazing?
The Anatomical Structure of Crypto Hashes
Exploring Hash Values and Their Uniqueness
What’s a crypto hash function? It’s like a secret code maker. In Bitcoin and other digital currencies, it turns transactions into unique sets of numbers and letters. This unique set is called a hash value. Think of it as a digital fingerprint for data.
Every hash value is one of a kind. No two transactions can have the same hash. If even a tiny bit changes in the transaction, the hash will change a lot. This is cool because it’s how people can tell if someone messed with any of the transaction data.
Hash functions are great for security. A good one like SHA-256 encryption, which Bitcoin uses, is tough to crack. The math behind it makes sure that no one can work backward to figure out the original data. This keeps your Bitcoin safe.
Ensuring Integrity with Cryptographic Hash Properties
Now, why do these hash values matter? Well, they help make sure everything stays in order. Cryptocurrency hashing explained in simple terms means taking info and scrambling it into a hash value. It must follow some rules, which are the cryptographic hash properties.
One key property is that it should be fast to make a hash from data but really hard to do the reverse. This is like a one-way street, where cars can only go one way. Another is that they’re hard to predict. This means the hash that comes out doesn’t seem related to the data put in.
These properties are why hashes keep your coins secure. They guard against two big problems: collisions and people trying to guess the original data, which we call preimage resistance in crypto. Collisions happen if two different bits of data give the same hash. Good hash functions like SHA-256 stop this from happening.
To mine new coins, like in Bitcoin or Ethereum, miners use these rules to solve puzzles. They guess numbers until their hash matches what the crypto network is looking for. This is called finding the nonce value. The search for the right hash is also tied to the hash rate, which is how many guesses a miner can make per second.
Miners who solve the puzzle get to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. Each block has its own hash and links to the hash of the last block. This is how we get a chain – hence, blockchain. This chain makes sure that if someone tried to mess with one block, we would know because all the other blocks would be wrong.
These processes use a lot of hash functions to keep the network secure. Choosing the right hash function is super important. It needs to be tough against attacks and keep hashes unique. This is why cryptographers are always looking for the best one.
In summary, hashes in cryptocurrency are there to make sure everything stays legit and secure. From creating unique transaction IDs to mining new coins, they are the superheroes of the crypto world. They take complex data and lock it down tight, so we can all trust that our digital money is in good hands.
The Nuts and Bolts of Cryptocurrency Mining and Security
Diving into Hash Rates and Their Significance in Mining
Imagine a race where computers solve puzzles fast. This is mining in crypto. Miners use powerful machines to solve math problems. When they win, they add new coins to the system. This race’s speed is the hash rate. It shows how quick a miner works. A higher hash rate means more chances to add a block and earn coins.
Hashing keeps the race fair. It turns data into a fixed size hash value. Like a unique fingerprint for data. No two are alike. This ensures every coin and transaction is one of a kind.
Mining uses a lot of power. Each guess for the puzzle is hashing. More guesses mean higher electricity. So, miners need to balance speed with cost. Only then can they win and not lose money.
Hash rates matter to everyone in crypto. A high rate makes the network strong against attacks. It’s like having more guards. The more miners, the more secure everything is. If the rate drops, it’s like guards leaving. The network could get hit by thieves.
In simple words, miners are puzzle solvers. Their tool, the hash rate, is key to winning coins and keeping our crypto world safe.
Enhancing Security Through Collision and Preimage Resistance
Hashing must be tough to break for good security. It should be hard to find two sets of data giving the same hash. We call this collision resistance. Imagine if two keys opened one lock. That’d be a big no-no. With a strong crypto hash function, no two data sets have the same hash key.
Preimage resistance is also key. It should be impossible to guess the data from its hash. That’s like trying to guess a whole apple pie’s ingredients by only sampling a crumb.
These two things stop cheats. They make sure that old data can’t be changed without notice. It’s like having unbreakable seals on files. SHA-256 is king here. It’s what secures Bitcoin. This is tough math that no computer can cheat. It locks down every coin and deal.
So, how does all this keep our crypto money safe? First, resistance stops copies. No two transactions can be the same. This keeps everyone’s coins rare. Second, it stops sneaky changes to records of who-owns-what.
In short, hash functions are like super guards. They use math to keep crypto safe and sound. It’s their rules, like collision and preimage resistance, that lock down our digital treasures. Without them, crypto would be wild and risky. But with them, we can trust our e-wallets just like we trust banks.
Behind the Scenes: Nonces, Hash Verification, and Public Keys
The Significance of Nonce Values in Achieving the Desired Hash
What is a nonce in cryptocurrency hashing?
“Nonce” stands for “number only used once.” A nonce is a random number in crypto used for hashing. Miners need it to solve hash puzzles and add new blocks to the blockchain.
When people talk about cryptocurrency hashing, they often mention the nonce. A nonce is a special number. In crypto, we use it once for creating a hash value that meets the network’s rules. To find it, miners try many nonces until they hit the right one. It’s like digging through a big pile of numbers to find a golden key. This key unlocks new blocks which is how miners get new coins.
The Role of Hash Functions in Transaction Verification and Public Key Cryptography
How do hash functions work with public keys to secure transactions?
Hash functions mix transaction details with a user’s public key. This creates a unique digital signature. That signature proves the transaction is valid and comes from the right person.
In any crypto deal, we use hash functions to check everything is on the up and up. They take information from the transaction and scramble it together with something called a public key. Every user has a public key, and it’s like a special ID that everyone can see. When they hash these two things together, it’s like sealing an envelope with a wax stamp that has the user’s unique mark. Now, no one can change what’s inside without breaking that seal. This keeps our crypto safe. It makes sure the digital money only goes where it’s supposed to.
This fuss about hashing isn’t just for show; it’s the guardian of crypto. The hash functions we use, like SHA-256, don’t just scramble data. They protect it, too. They make it near impossible for anyone to mess with your hard-earned crypto. Each time you do something with your digital coins, this kind of encryption puts its foot down and says, “This has got to match.” And if it doesn’t, it’s like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole. It just won’t work.
So, here we have this amazing toolbox filled with things like the nonce value, hash verification, and public keys. They’re not just fancy words. They’re the power tools keeping crypto strong and steady. Using these tools right, we get a network that’s as tough as nails. It won’t let the bad guys mess with it. And for anyone with crypto dreams, that’s a big deal.
By now, you should feel a bit like a detective who’s just cracked the case. You’ve got the inside scoop on how this digital world ticks. The nonces and the hashing, they’re not just cogs in the machine. They’re the heroes keeping our crypto flying high and secure. And you know what? Next time you hear someone talking crypto, you can jump right in. You’ve got the know-how, thanks to these nuggets of wisdom on nonces and hash functions. Keep these secrets in mind, because they’re locking down the vault of your virtual treasure.
We’ve explored the key parts of hashing in cryptocurrency. Starting with hash functions, we saw how they secure the blockchain, especially with the SHA-256 in Bitcoin. We then peeked inside crypto hashes, learning how unique hash values are and why they matter.
We also looked at mining and security, learning about hash rates and how they affect mining. We know now that collision and preimage resistance bolster security. Lastly, we delved into nonces and public keys, seeing how they help achieve the right hash and keep transactions safe.
Remember, hashing is vital. It keeps your crypto transactions secure every step of the way. From unique hash values to mining and nonces, each part works together to guard your digital treasures. Keep this in mind next time you make a transaction or mine new coins. It’s tech at its finest, ensuring your crypto moves are safe and sound!
Q&A :
What Exactly is Hashing in the Context of Cryptocurrency?
Hashing in cryptocurrency refers to the process of taking an input (or ‘message’) and using a mathematical function (hash function) to produce an alphanumeric string, typically of a fixed length, known as the hash value or hash code. This technique is fundamental in maintaining the integrity and security of blockchain technology, ensuring that transactions and blocks are immune to tampering and fraud.
How Does Hashing Secure Cryptocurrency Transactions?
Hashing secures cryptocurrency transactions by creating a unique hash for every transaction that is nearly impossible to replicate. When a transaction is hashed, it is timestamped and added to a block in the blockchain. If a hacker attempts to alter a transaction, the hash would change, signaling a discrepancy in the network. This aspect of hashing makes cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin secure from fraudulent activities.
Can Hashing Be Used to Reverse Engineer Cryptocurrency Data?
No, hashing is a one-way function, meaning it is computationally infeasible to reverse the process. This characteristic is crucial for maintaining privacy and security within the blockchain. Hashes act like digital fingerprints for data, where the original information cannot be easily deciphered from the hash itself, protecting user data and transaction details.
What Hash Functions are Commonly Used in Cryptocurrency?
Various hash functions are used in cryptocurrency, with SHA-256 being one of the most prominent due to its use in Bitcoin. Other cryptographic hash functions include RIPEMD-160, Keccak (SHA-3), and Scrypt, each serving different cryptocurrencies and purposes, but all aiming to provide security and stability to the decentralized ledger system.
Why is the Process of Hashing Integral to the Proof of Work System?
Hashing is integral to the Proof of Work (PoW) system, which is utilized by many cryptocurrencies, as it facilitates the competitive process of mining. In PoW, miners compete to find a hash below a target value set by the network, which requires significant computational effort. The first miner to achieve this can add a new block of transactions to the blockchain, for which they are rewarded. Hashing thereby underpins the security and trustless nature of cryptocurrency by ensuring new blocks are created through a robust, decentralized consensus mechanism.