Unveiling the Mystery: What Is Distributed Ledger Technology in Blockchain?
Have you ever wondered what is distributed ledger technology in Blockchain? Some say it’s the backbone of a new Internet, others claim it’s the most revolutionary technology since the web itself. But let’s cut through the noise and make sense of this digital ledger. As an expert, I’ll lead you straight into the world of DLT, where every participant holds the power of the ledger.
We’ll explore how it drives blockchain, the trust it builds without middlemen, and why its transparency is a game-changer. So if terms like ‘blockchain’ or ‘cryptocurrency’ leave you scratching your head, sit tight. I’m here to lift the veil on the digital world’s secret sauce, one digestible piece at a time.
Deciphering Distributed Ledger Technology in Blockchain
Core Principles and Operation of DLT
You’re about to crack the code of DLT in blockchain. It’s much like a shared notebook. Imagine if all your friends wrote in the same book. Each page of notes must match. That’s the heart of DLT.
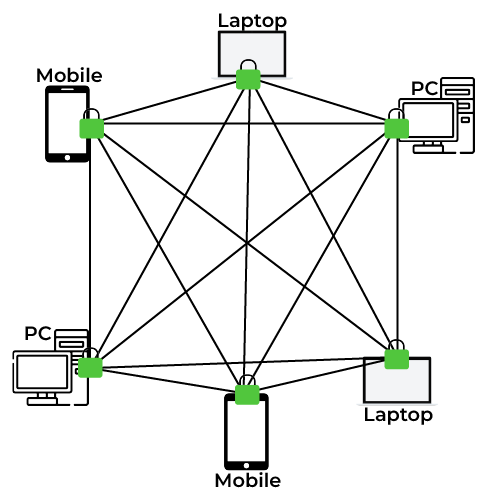
Every person holds a copy of this digital notebook. When someone writes in it, everyone’s copy updates. No one person can change things alone. Everyone must agree, or there’s no update. This trust we build is key to DLT’s power.
Now, how does it work? It uses clever math and rules. Each new page has a unique stamp, called a hash. This ensures no mix-ups.
It’s like a game where everyone follows the same rules. If you play fair, transactions are smooth. These rules are the principles behind DLT. Simple yet effective.
Distinguishing Blockchain from Broader DLT Concepts
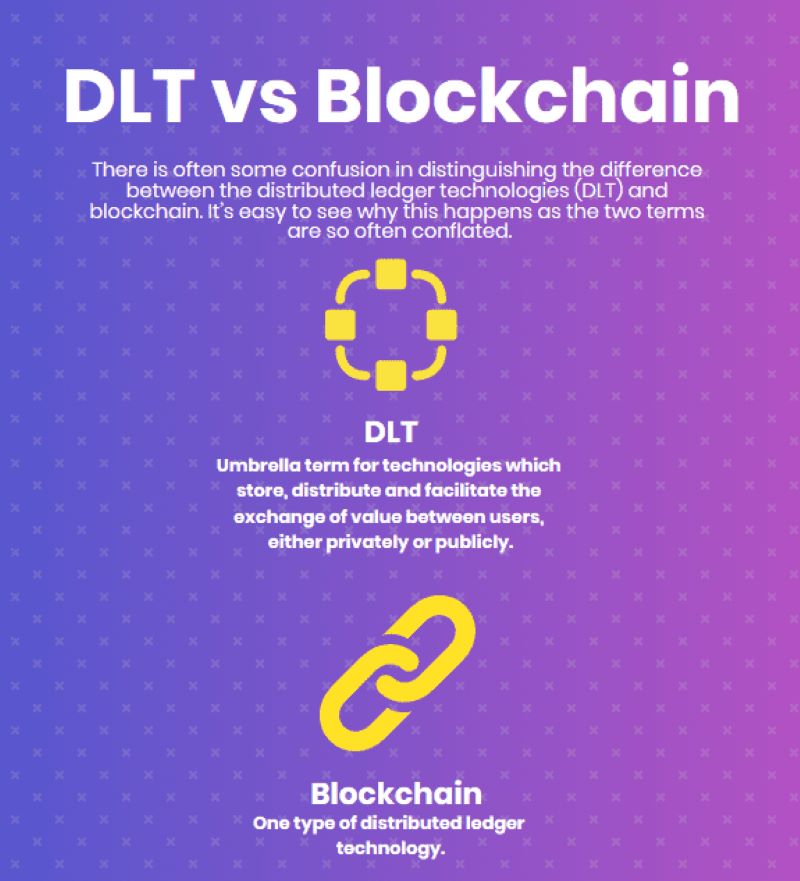
So, is blockchain different from DLT? Yes, a bit. All blockchain is DLT, but not all DLT is blockchain. Let’s make sense of this.
Blockchain is a type of DLT with extra bits. It adds blocks of data linked in a chain. This gives a clear order to our notes. It makes sure what’s past can’t be changed with ease.
But DLT isn’t just blockchain. There are many types. Each with its own style. Some ledgers are open for all to read and write. Others set up rules on who can join. Imagine playgrounds with different games. Each ledger is its own game.
Now, let’s talk about keeping everyone honest. In the world of DLT, we call this consensus. It’s a fancy term for agreement on what’s true. With the right rules, bad players can’t spoil the game. These mechanisms help keep our shared notebook in check.
When you hear about blockchain transactions, think of DLT. They are like notes we pass in our digital notebook.
In a nutshell, DLT is a smart way to track and agree on information. It helps us to keep everything fair and square. It’s transforming how we do things. From money to keeping track of things we buy and sell. It paves the way for new ideas, like smart contracts that make deals on their own.
Imagine a world where trust comes easy. That’s the world DLT is building, one digital step at a time. It’s a change for the better, making sure what we agree on stays agreed upon.
As we explore this tech, remember its essence. It’s a shared, trustworthy system that’s shaking up how we connect. And that, my pals, is the heart of DLT unlocked.
The Building Blocks: Understanding How Blockchain Employs DLT
The Role of Consensus Mechanisms in DLT
People often mix up blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT). To clear things up, DLT is a wider tech that blockchain is part of. DLT lets us record info in many places at once. In simple words, this means that everyone on a network can have their own copy of a shared ledger. Now, blockchain is special with its own terms. You know, it’s like a type of DLT but has extra cool features. For blockchain, trust is key, and this is where consensus mechanisms come in.
Consensus mechanisms are rules. They help all network users agree on ledger content. Picture kids on a playground deciding which game to play. They vote and the game with the most votes wins. That’s how blockchain time-stamps and approves data, by voting. Different blockchains use different voting rules. They make sure everyone agrees with the changes made. No single player or computer makes changes alone. They work as a team, only moving forward when there’s a green light from the group.
Blockchain Data Structure Intricacies
Now, let’s get into some nitty-gritty: blockchain’s data layout. Think of blockchain as a train made of data wagons, we call them blocks. Each block is like a page in a ledger or a line in a list. They’re linked or ‘chained’ together by special math codes, kind of like secret handshakes between them. Once a block is full of transactions, another one starts. The cool thing? You can’t just rub something out. If you try to mess with one, everyone can tell because the handshakes won’t match up.
These blocks also have unique IDs, fancy term alert: hash functions. A block’s ID changes if someone tries to tweak it. It’s like a protective seal on your snacks, break the seal and everyone knows. Blocks have a public life, always visible. But they guard their contents with tough-to-crack codes. So, while everyone sees the blocks, knowing what’s inside is a tougher nut to crack.
DLT’s superpower is its shared, no central boss feature. This means no single computer calls the shots. It’s a team effort, which makes things safer and fairer. Let’s circle back to those playtime rules. No kid is the boss, and they all need to nod yes before playing a game. This way, no single kid can spoil the fun. It’s the same for blockchain, which makes it a tough nut for sneaky folks to crack.
What this boils down to is trust without needing a middleman. You don’t need a bank or a company to say a transaction is OK. Instead, the network’s joined power does that, stamping its foot down saying, “Yep, this is legit!”
In short, when people chat about blockchain, they’re seeing DLT in action, using fancy math, group rules, and teamwork to keep things in check. It’s like a community garden. Everyone works together, making sure it thrives, staying true to the shared dream of a safe and open space for exchanging valuable stuff.
Types and Uses of Distributed Ledgers in Blockchain Networks
Exploring Public, Private, and Consortium Blockchains
Imagine a special notebook. This notebook lets lots of people write in it. But, once written, no one can erase it. This is like a distributed ledger. It is a shared, fixed record. We use it to note things like money trades and who owns a house. Now, let’s talk about three main types.
First, public blockchains are like a notebook anyone can use. They are open and let anyone join and see what’s inside. Bitcoin and Ethereum are like this. They are big, open spaces where anyone can take part.
Next, private blockchains are like diaries. They are closed. Only some people can read or write in them. Big companies like these. They keep their data safe but can share things inside their group.
Last, we have consortium blockchains. These are like club notebooks. A few groups agree to share this notebook. They make rules on who can see and write in it. This is great for business deals that need trust but not everyone involved.
In each type, DLT in blockchain helps make sure everything’s correct. Everyone has a copy of the notebook. So, all copies must match for something new to write down.
Now, these different types are perfect for many uses. Public ones let people make and send digital money, like Bitcoin. Private ones help a single group, like a bank, move money fast and safely. And consortium ones can help many businesses work together, like tracking stuff as it moves around the world.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies of DLT
So, how do real people use distributed ledger systems? Lots! For one, we have smart contracts. These are like deals that can do things themselves. When a thing happens, they just start. Like, a smart deal might pay for a delivery automatically when it arrives.
Other uses? Well, some put house titles on ledgers to stop fake claims. In music, artists use them to get paid straight away when someone plays their song. Farmers in some places use them to sell their goods easily and get paid quick.
What’s more, some folks find DLT vs traditional databases really useful. Why? Because they spread out the info. This means no one single point can break, and all info is correct.
DLT technology providers are now all over, offering ways to use this tech. They make systems that can handle trades, health records, even votes!
In the end, though, it’s about trust. Distributed ledgers in blockchain networks mean trust. When things are clear and we can see where our stuff goes, it’s easy to trust the process. And as we build more smart contracts in DLT, and get better at handling lots of info, we’ll see this tech do even more!
Remember, all this cool stuff works because of special math called cryptographic principles. This math makes sure our notebook stays safe, and no one can cheat. It’s the secret sauce that makes blockchain transactions safe and DLT so great! From farming to voting to music, distributed ledger technology is changing our world!
Advancing the Future: Innovations and Challenges in DLT
Enhancing Scalability and Performance in Blockchain Systems
Scalability is a big word in the world of distributed ledger technology, or DLT. When we say a blockchain system is scalable, we mean it can handle lots of work even as it grows. Right now, some blockchains are slow and can’t take on much at once. To fix this, experts like me are working on new ways to make them faster and able to do more.
One way is by changing how transactions are checked. Instead of every computer in the network saying “OK” to a transaction, only a few might need to. This can speed things up a lot. We’re also looking at how to make data smaller, so there’s less to check and move around.
By doing these things, blockchain could one day be as smooth as buying a candy bar at the store. Just grab, pay, and go – quick and easy!
The Importance of Security and Cryptography in DLT
Now, let’s chat about keeping your stuff safe in DLT. Imagine locking up your bike with a magic lock that only you can open. That’s a bit like how security in DLT works. We use math puzzles, called cryptography, to lock up the data. This keeps it safe from people we don’t want messing with it.
Every bit of info on a blockchain has its own special lock. To open it, you need a secret key that matches. Only the right key can unlock the data. This way, even if someone else gets their hands on the lock, they can’t open it without that key.
But wait – there’s more! Each piece of data is chained to the next. So if someone tries to change one, it messes up all the rest. That’s blockchain immutability. It’s like a game of dominoes. Push one, and they all fall down!
One challenge, though, is that cyber bad guys are getting smarter. They’re always looking for ways to break our math puzzles. So, we keep having to make new, tougher puzzles. It’s like a never-ending battle of wits between good and bad hackers.
What we aim for is a super secure DLT that can still be fast and smooth. It should lock up our digital treasures tight, but also let us get to them easy when we need to.
By tackling these challenges, we’re pushing blockchain into an exciting future. Imagine buying a house with a tap on your phone or voting from your couch. That’s where we want to go, and I’m right here, working to make it happen. Keep an eye on us – the blockchain builders – we’re creating a world where DLT changes the rules of the game!
We’ve walked through the complex world of distributed ledger technology (DLT) and its roots in blockchain. We explored the core ideas and how DLT runs, and then looked hard at how blockchain stands out in the DLT family. We learned how blockchain uses DLT, from consensus methods to the unique way it stores data. We saw how different types of ledgers—public, private, and consortium—change the game and checked out real-world spots where DLT is making waves.
To close, this tech keeps leaping forward, bringing new chances and tough hurdles. From faster, stronger blockchains to keeping them safe with crypto, DLT is not just tech talk—it’s shaping our world. Keep an eye on it; the best is yet to come!
Q&A :
What exactly is distributed ledger technology in blockchain?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) refers to a digital system for recording transactions of assets in which the transactions and their details are recorded in multiple places at the same time. Unlike traditional databases, DLT has no central data store or administration functionality. In a blockchain, which is a type of DLT, the ledger is maintained across a network of nodes, making it highly resistant to fraudulent activity and cyber threats due to its consensus mechanisms and cryptographic security.
How does distributed ledger technology work within the context of blockchain?
Within blockchain, distributed ledger technology works by spreading the information across a network of interconnected computers, or nodes, each of which contains a copy of the ledger. Every time a transaction is made, it is transmitted to the network and validated through a process known as consensus. Once a transaction is confirmed, it is grouped into a block with other transactions, and this block is then cryptographically linked to the preceding block, effectively creating a chain. This structure ensures data integrity and immutability.
What are the main benefits of using distributed ledger technology in blockchain?
The main benefits of using distributed ledger technology in blockchain include enhanced security, improved transparency, and reduced chances of data tampering. Its decentralization ensures that no single entity has control over the entire network, which can prevent fraud and corruption. The ledger is also transparent to all participants with the required permission, fostering trust among users. Additionally, since the data is immutable, once recorded on the blockchain, the history of asset transactions can be audited and verified, which is valuable for compliance and regulatory purposes.
How is distributed ledger technology different from traditional databases?
Distributed ledger technology is different from traditional databases in its structure and governance. Traditional databases are centralized, meaning the data is stored and managed from a single location or by a single entity, creating a point of vulnerability. In contrast, DLT is decentralized and each participant on the network has access to the entire database and its complete history. Furthermore, DLT employs consensus algorithms that require validation by multiple parties before a transaction can be added to the ledger, enhancing security and trustworthiness.
Are there different types of distributed ledger technology besides blockchain?
Yes, there are different types of distributed ledger technology besides blockchain. While blockchain is the most recognized and widely implemented form of DLT, other types include directed acyclic graph (DAG) technology, which is used by some cryptocurrencies for faster transaction speeds and scalability. There are also permissioned ledgers, where the access to the ledger is controlled by a select group of entities. Each type of DLT has its own features and use-cases, catering to different requirements of industries and projects.