In the world of blockchain technology, the term DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is gaining increasing attention due to its ability to overcome the limitations of traditional blockchain systems. So, what is DAG Blockchain, how does it work, and why is it highly regarded in fields such as finance and the Internet of Things (IoT)? This article will provide an in-depth look at this innovative technology.
What is DAG Blockchain?
DAG Blockchain (Directed Acyclic Graph Blockchain) is a special type of data structure used in distributed ledger technology. Unlike traditional blockchain, which uses sequentially linked blocks, DAG is based on a Directed Acyclic Graph structure. In this structure, transactions are directly linked to each other, not following a linear order as in traditional blockchain.

Key features of DAG Blockchain
To better understand “What is DAG Blockchain?” we need to explore its key features. DAG Blockchain offers many characteristics that make it an ideal choice for modern applications. Here are the important features:
- Elimination of mining requirements: One of the biggest advantages of DAG is that it does not require mining to validate transactions. In traditional blockchain, transaction validation depends on miners through consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work (PoW), which leads to high costs and resource consumption. DAG removes this entirely by allowing each transaction to validate previous transactions, reducing operational costs and being more environmentally friendly.
- Parallel transaction processing: DAG allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously rather than in a linear sequence like traditional blockchain. This is particularly useful when dealing with a large number of transactions. This feature not only speeds up transaction processing but also reduces the risk of network congestion.
- Superior scalability: In traditional blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum, network performance can significantly decrease as the number of transactions increases. However, with DAG, adding new transactions actually enhances the overall system’s performance, thanks to its distributed validation structure.
- Low or zero transaction fees: Since DAG does not require miners or block rewards, transaction fees are almost eliminated. This is a major advantage, especially for applications that need to process small transactions (micropayments).
- High decentralization: DAG leverages the power of a decentralized network. Each node acts as an independent validator, ensuring the system’s security and transparency without the need for intermediaries.
With these features, DAG Blockchain not only provides technical efficiency but also opens up wide application potential across various industries.
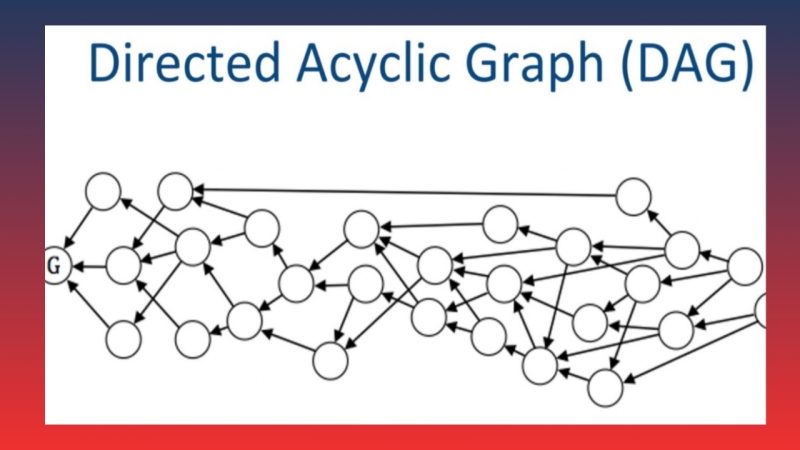
How DAG Blockchain works
The operation mechanism of DAG Blockchain is designed to optimize transaction speed and processing performance. To understand it better, let’s examine the key steps in this process:
- Transactions represented by vertices: Each transaction in DAG is represented as a vertex (node) in the graph. A new vertex, when created, links to previous vertices, i.e., earlier transactions. This ensures that every transaction in the system is validated.
- Transaction validation: Instead of relying on miners as in traditional blockchain, in DAG, each new transaction must validate one or more previous transactions. This reduces dependency on traditional consensus mechanisms and speeds up the validation process.
- No fixed chain: One significant difference of DAG compared to traditional blockchain is the absence of a linear order. New transactions do not need to queue up for validation but can occur simultaneously in multiple positions on the graph.
- Decentralized consensus: DAG uses a peer-to-peer consensus mechanism where each node in the network can participate in validating transactions. This ensures decentralization, security, and transparency for the entire system.
Thanks to this operational mechanism, DAG Blockchain not only addresses performance issues but also opens up possibilities for environments that require fast transaction processing, such as IoT and payment systems.

Differences between DAG Blockchain and traditional Blockchain
DAG Blockchain and traditional Blockchain are both distributed ledger technologies, but they have distinct characteristics, catering to different needs in the industry. Here are the key differences between the two:
- Data structure: Traditional blockchain uses a chain-like data structure, where transactions are grouped into blocks and linked together sequentially. Each block contains information about the previous one, forming an immutable chain. In contrast, DAG Blockchain is built on a directed acyclic graph where each transaction is a point in the graph and directly links to previous transactions. This structure removes the chain constraints and allows parallel transaction processing.
- Transaction validation mechanism: In traditional blockchain, consensus mechanisms such as Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS) require miners or validators to add transactions to the chain. This process is often time-consuming and resource-intensive. On the other hand, DAG Blockchain does not use blocks or miners. Each transaction in DAG self-validates one or more previous transactions, minimizing wait times and eliminating the need for centralized consensus.
- Transaction processing speed: The transaction processing speed of traditional blockchain is limited by the block creation process, especially in large networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum. In contrast, DAG Blockchain allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, improving validation speed and reducing the likelihood of congestion as the network expands.
- Scalability: Traditional blockchain often struggles with scalability as transaction volume increases, leading to high transaction fees and longer confirmation times. DAG Blockchain addresses this issue by increasing network performance as more transactions are added, thanks to its distributed validation mechanism.
- Transaction fees: In traditional blockchain, transaction fees are often high due to mining costs and block rewards. In DAG Blockchain, these fees are nearly nonexistent or very low, as mining is not required, and no block rewards are involved. This is particularly appealing for applications requiring frequent small transactions, like micropayments.
- Use cases: Traditional blockchain is well-suited for large data storage applications, smart contracts, and traditional financial systems like Bitcoin or Ethereum. In contrast, DAG Blockchain excels in fields that demand high transaction speeds, such as IoT, instant payments, and modern decentralized finance (DeFi) systems.
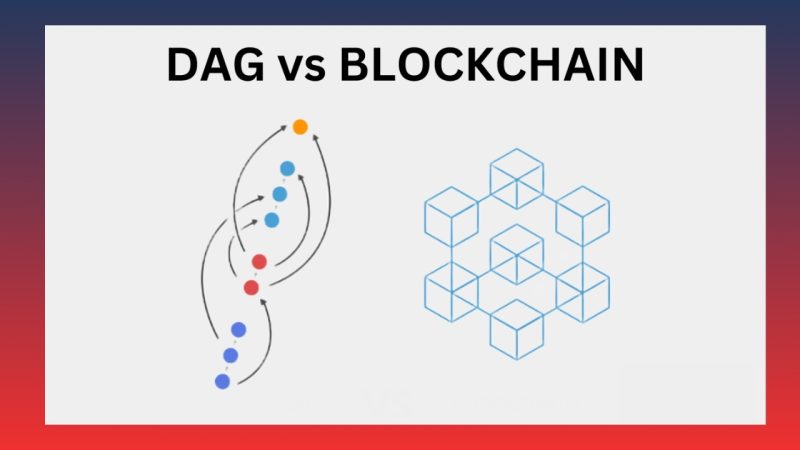
Thus, both DAG Blockchain and traditional blockchain play important roles in technology, but their differences in structure and operation make each suitable for different goals and applications. DAG Blockchain is emerging as the optimal solution for systems requiring speed, low costs, and superior scalability.
Practical applications of DAG Blockchain
IOTA – IoT technology
IOTA is one of the most notable applications of DAG Blockchain. This project uses Tangle, a special type of DAG, to address the issues faced by traditional blockchain, such as high transaction fees and poor scalability. IOTA is particularly well-suited for the Internet of Things (IoT), where millions of devices need to exchange data quickly and efficiently.
Applications:
- Connecting IoT devices in environments such as smart cities, autonomous transportation, and other applications.
- Data exchange between devices without transaction fees, optimizing costs.
Nano – Instant payments
Nano is a payment platform that uses Block-Lattice, a type of DAG structure, to enable instant transactions without any transaction fees. With the advantage of no mining, Nano processes transactions quickly and efficiently, making it an ideal choice for micropayments.
Applications:
- Nano has been used for daily payment transactions, with the ability to process instant transactions between individuals and businesses.
- Suitable for applications like in-game payments, online services, and DeFi platforms.
U2U Network – Modern DeFi infrastructure
U2U Network, aiming to develop infrastructure for the Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN) ecosystem, uses DAG to optimize interactions between decentralized applications (dApps) and blockchain. With high scalability and low transaction fees, U2U Network can support a large number of transactions in DeFi applications and other technological fields.
Applications:
- U2U supports DeFi platforms, gaming, and other blockchain applications, providing smooth and efficient connectivity between chains.
- Services like U2U SDK and U2U phone use DAG to enhance transaction efficiency and user interaction.
Hedera Hashgraph – Optimizing Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Hedera Hashgraph is a prominent project using DAG to optimize transactions in Decentralized Finance (DeFi). The Hedera Hashgraph network uses the Gossip about Gossip consensus mechanism combined with Virtual Voting to maintain network integrity and security without the need for energy-intensive mining.
Applications:
- Facilitates fast and secure financial transactions in DeFi applications.
- Products like Hedera Consensus Service (HCS) offer consensus services for businesses and organizations in industries such as banking and finance.
Constellation – Managing Big Data
Constellation Network is a blockchain platform based on DAG aimed at optimizing big data management and analysis. By using DAG, Constellation can efficiently handle distributed data and reduce operational costs, making it ideal for businesses and organizations that need to manage large, complex data sets.
Applications:
- Industries such as finance, healthcare, and insurance can leverage Constellation to store and analyze big data in real-time.
- Organizations needing to ensure data integrity and security in distributed systems.
The Graph – Decentralized data query system
The Graph is an application using DAG to optimize data querying in decentralized applications (dApps). Rather than searching through a centralized database, The Graph uses a DAG-based system to distribute and retrieve data quickly.
Applications:
- Serves dApp developers in efficiently querying data from blockchains.
- Improves data searching and analysis capabilities in blockchain ecosystems, helping decentralized projects like Uniswap, Aave, and other DeFi applications run smoothly.
DAG Blockchain represents a breakthrough in distributed ledger technology, standing in stark contrast to traditional blockchain. With its efficient operational mechanism, no mining requirement, and ability to process parallel transactions, DAG has shown great potential in solving scalability and transaction cost issues.
Crypto Currency Bitcoin Price hopes this article has helped you understand “What is DAG Blockchain?” Don’t forget to follow ABC for more updates and insights every day.
