Dive into the core of crypto tech with me! You’ve likely heard buzz around Bitcoin and Ethereum, but have you wondered what is a layer 1 blockchain? It’s the rock-solid ground that powers those coins. Think of it like the electricity that lights up your home. Just as the wires and power grid are essential, these blockchains keep your digital transactions safe and sound. They do it all – create new coins, check transactions, and make sure everything’s secure. Ready to get the full scoop on these crypto powerhouses? Let’s dig in and reveal their secrets!
Understanding the Foundation of Layer 1 Blockchains
Exploring Blockchain Basics and Protocols
Think of a blockchain as a magic book. Each page in the book is a block. This book grows as more pages or blocks are added. It’s a list of records, all linked together. It’s also very open. Anyone can read it. Crypto coins like Bitcoin are just one thing a blockchain can keep track of. But it’s not just for money. It can hold many types of info.
Blockchains are like games with rules. These rules are called protocols. They make sure everyone plays fair. If someone tries to cheat, the rules catch them. Imagine we’re playing a card game. The rules say you can’t hide cards. In blockchain, if the rules find a hidden card, they say “No way!” and kick that out.
These protocols also have special math problems. They protect the blockchain. They help in storing the info safely.
Comparing Layer 1 vs Layer 2 Technologies
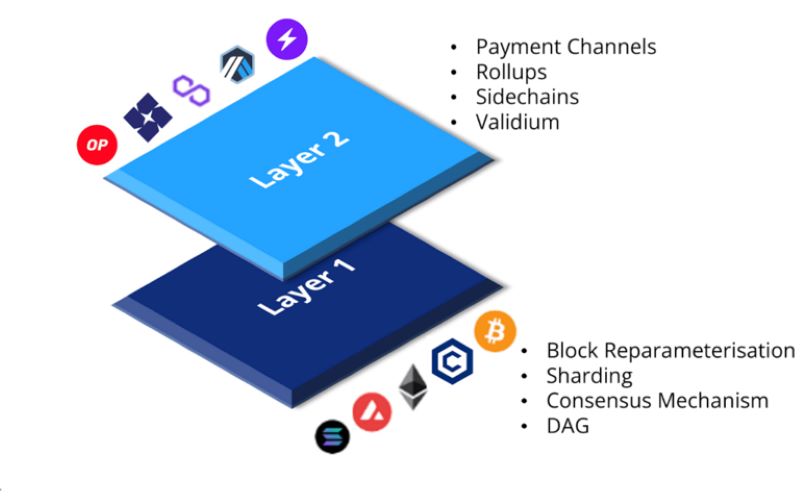
Now, let’s talk about layers. Think of a cake with two layers. Layer 1 is the first, bottom layer. It’s the base of a blockchain, like Bitcoin. It’s where the rules, coins, and all the action lives. Layer 1 must be strong and able to handle a lot of stuff. If not, everything on top falls down.
Layer 2 is like the frosting and decorations on top. This layer helps the base handle more traffic, like more people playing our game. It makes things run faster without changing the first layer’s rules.
Blockchain can be a bit slow and cost a lot to use. Layer 2 tries to fix these problems. It’s like finding a way to invite more friends to our game without crowding the room.

Layer 1 and Layer 2 work together to make sure everything runs smooth and safe. They are friends, helping each other to manage the game with as many players as possible.
In this magic world of blockchain, there are many ways to play the game. Some ways are well-known, and some are new magic tricks. For people who make these games, like me, it’s fun to invent new ways to make the game better!
We use our knowledge to solve big puzzles called the scalability trilemma. This trilemma is about making sure the game is fair, works well, and is safe for more and more people to play.
So, that’s how Layer 1 blockchains are the starting ground for all these exciting things we can do in the digital world! They make sure we have a solid and safe base to build on, like the foundation of a house or the first, main layer of our cake! And by understanding this, you get to see how important and cool this technology really is.
The Mechanisms That Drive Layer 1 Blockchain Networks
Digging into Consensus Mechanisms: Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
What’s the heart of a blockchain, you ask? It’s the way it makes sure all transactions are true. This is called a consensus mechanism. There are two main types: Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). Let’s break them down.
PoW is like a race where miners solve tough puzzles using powerful computers. The first to solve it gets to add a new block of transactions and is rewarded. It’s used by Bitcoin and is known for its firm security. But it uses lots of power, which isn’t great for our planet.
On the flip side, PoS is like having a lottery where the more coins you hold, the better your chances of being chosen to create a new block. It’s like a savings account that rewards you with the task of adding to the ledger and getting some coins in return. It uses much less power than PoW.
Both these mechanisms are key to keeping the network safe and running without a boss.
The Role of Network Participants: Mining and Validators
What roles do people play in keeping a blockchain going? There are miners and validators.
Miners are the tough workhorses in PoW. They use their gear to crack puzzles and keep the chain going. It’s through this process they create new coins, a bit like digital gold miners.
Validators have a different job in PoS systems. They’re like guards. They put their own coins up as a promise they’ll be good. If they try any funny stuff, they lose their coins. This way, they help keep everything in check.
In each kind of system, these participants work hard to secure the chain. They check the work, agree on what’s true, and earn rewards for their role. This creates trust in a trustless system, which means even if you don’t know the person on the other end of your transaction, you can feel safe.
In a layer 1 blockchain, all this action happens on the main network. This is the home base where transactions are final. It’s the strong foundation for all the exciting things built on top.
Remember, these processes are not just technical. They’re about people joining forces to make a system that’s fair and strong. And that’s what makes the world of blockchain so revolutionary.
The Role of Layer 1 Blockchains in Advancing Decentralized Applications
Deploying Smart Contracts on Platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum
Layer 1 blockchains make magic happen. They let us play with smart contracts. They’re like the soil where digital trees grow – strong and wide. Bitcoin was first to show up at the party. Now, Ethereum has taken the lead with even smarter contracts. Think of smart contracts like vending machines. You pick a snack, pay up, and ta-da! Out comes your treat. With smart contracts, you get to do deals without worry. Say you want to buy a game online. The smart contract makes sure you pay and get your game, easy peasy.
Ethereum is the cool kid on the block(chain). It’s got tools and tricks that make developers smile. These tools let them build all kinds of apps – we call them dApps. From games to money-sharing, dApps do it all. With Ethereum, if you can dream it, you can dApp it!
Bitcoin’s smart contracts are simpler but still cool. They keep track of who owns what in Bitcoin world. This basic type is good for some stuff, not others. Yet, it’s strong and tested, like an old tree that stands tall in a storm.
So, here’s the deal. Layer 1 blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are the backbone of smart contracts. They let you make deals in a snap. Oh, and the best part? These deals are as solid as rock, no going back. That means trust is built right in. You don’t need to cross your fingers or hope someone keeps their word. The blockchain does the heavy lifting for you. This is why smart contracts on these platforms are a big deal for apps that value trust and ease.
Ensuring Blockchain Security and High Transaction Throughput
Layer 1 blockchains aren’t just about making deals. They’ve got a tough job: keeping everything safe and fast. Imagine a city where every car runs smooth and no one ever breaks in. That’s what Layer 1 blockchains aim for. They use special codes and rules, we call them blockchain protocols, to keep everything secure.
Security is king. No one likes a hacker messing up their stuff. These blockchains use something called consensus mechanisms. They’re like a council of wise folks deciding what’s true. Everyone checks the work, so no one can cheat. It’s like having a bunch of referees in a game, always watching.
Now, consensus comes in different flavors. There’s Proof of Work – it’s like solving a big puzzle to prove you’re not lying. And there’s Proof of Stake – where you show trust by putting money on the line. These help keep the blockchain honest and safe.
But what about speed? Everyone hates waiting. Layer 1 blockchains work on that too. They’re finding ways to handle more deals at once. This is called transaction throughput. More throughput means less wait, more doing.
They’re getting better at this all the time. Techniques like sharding are like opening more lines at a store. It means more people can buy stuff at the same time. These solutions help networks deal with lots of users without breaking a sweat.
In the end, Layer 1 blockchains are the heroes behind the scenes. They give power to smart contracts while watching out for safety and speed. They’re the starting point for all the amazing things we do with crypto and dApps. And as we dream up new apps, Layer 1 blockchains keep pushing to be better, faster, and stronger.
Scaling Layer 1 Blockchains to Meet Future Demands
Addressing the Scalability Trilemma Through Advanced Solutions
What is the scalability trilemma? It’s a tough problem in blockchain. It deals with keeping a perfect balance between three big things: security, decentralization, and speed. With Layer 1 blockchains, like the ones Bitcoin and Ethereum use, it’s a huge deal.
So, how do we fix this trilemma? One way is with a sharding technique. This means splitting the blockchain into smaller pieces called shards. Each shard holds its own piece of the network’s transactions and smart contracts. This way, the network can process more things at once. It’s like having more lanes on a highway – less traffic jams!
Some folks also think about layer 1 solutions where the rules of the blockchain can change based on how much it’s being used. This could help networks manage heavy traffic better. Lastly, direct chain communication is a cool idea where different blockchains talk to each other. This could make everything much smoother and open doors for new ways to use blockchains together.
Balancing Network Fees and Block Generation Rate for Optimal Performance
Now, let’s talk money and time, or network fees and block generation rate. First off, what’s a network fee? It’s like a tiny ticket price you pay to send your cryptocurrency. Miners or validators who keep the network safe get this fee.
But high fees can make folks unhappy. That’s where a smart balance comes in. Too high, and people won’t want to use the blockchain. Too low, and miners might not think it’s worth it. It’s a fine line to walk.
The block generation rate is how fast new chunks of data, or blocks, are made. Faster rates mean more transactions and smart contracts can go through. But it can also mean a busy network with possible mistakes. Slower rates are safer, but they might test your patience.
Layer 1 blockchains need to find that sweet spot. It’s like being Goldilocks trying to get everything just right — not too hot, not too cold, but perfect to keep everyone in the game.
So, in short, we’ve got some smart people tackling the big challenge of making Layer 1 blockchains ready for more action. They’re making sure that, as things heat up with more people and more uses, our blockchain basics hold strong. They’re mixing the right ingredients — from sharding to fee strategies — to whip up a recipe for a blockchain that’s secure, fast, and open for everyone. That’s the future we’re building, one block at a time!
Let’s recap what we covered! We kicked off by getting to grips with layer 1 blockchains. We looked at how they differ from layer 2 and why that’s key for tech gurus like us. Then, we dove into the nitty-gritty, exploring how these networks stay secure and truthful with proof of work and proof of stake. Remember how miners and validators keep things ticking? Vital stuff.
Next up, we saw how smart contracts run on platforms such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, pushing the boundaries of what apps can do without the middleman. Security and speed are must-haves for these systems, and we got why they’re non-negotiable for a smooth ride.
Finally, as we look ahead, layer 1 blockchains must grow to serve more people. It’s a tough nut to crack – keeping things swift, secure, and not too pricey. But by tackling the scalability trilemma and juggling costs and block creation, our net can get only stronger.
My final thoughts? Keep on layering! The future looks bright with these tech marvels paving the way for a world where you and I call the shots. Let’s step into tomorrow ready to innovate and grow. Onwards and upwards!
Q&A :
What Constitutes a Layer 1 Blockchain?
Layer 1 blockchains form the foundational structure of a cryptocurrency network. They are the main framework that supports all on-chain activities like transaction processing, consensus mechanisms, and data storage. Examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other standalone blockchains.
How Does a Layer 1 Blockchain Differ from Layer 2 Solutions?
While Layer 1 refers to the underlying main blockchain architecture, Layer 2 solutions are secondary protocols built on top of the main blockchain. Layer 2 aims to enhance scalability and transaction speed by handling transactions off the main chain, which can help to alleviate congestion and reduce fees.
Why is Scalability Challenging for Layer 1 Blockchains?
Scalability is a significant challenge for Layer 1 blockchains because they often have a limited capacity for processing transactions within a certain time frame. As the network grows and transaction volume increases, these blockchains can become congested, leading to slower transaction times and higher fees.
What are the Most Common Consensus Mechanisms in Layer 1 Blockchains?
The most prevalent consensus mechanisms used in Layer 1 blockchains are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). PoW, used by Bitcoin, relies on miners to validate transactions through computational work. PoS, an alternative used by many newer blockchains, enables validators to secure the network based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as a form of collateral.
How are Layer 1 Blockchains Enhancing their Scalability?
Layer 1 blockchains are exploring various scalability solutions such as sharding, where the blockchain is divided into smaller pieces, or shards, that can process transactions and smart contracts in parallel. Additionally, there are updates and innovations like Ethereum’s transition to PoS and the introduction of side chains that operate alongside the main chain to increase its capacity for processing transactions.
