Imagine a crypto system where your coins do more than just sit in your wallet. Welcome to what is delegated proof of stake in crypto—a transformative approach to blockchain governance where your vote shapes the network. With Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), you’re not just an investor; you’re an active participant in electing the gatekeepers of your digital world. Dive in as we decode how DPoS sets itself apart from the pack, promising more power in your hands and a sleeker chain response under the hood. Ready to see what making a real-world impact looks like in the virtual currency realm? Let’s unearth the future of blockchain democracy.
Understanding Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
The Fundamentals of DPoS
Delegated Proof of Stake, or DPoS, shakes up traditional crypto rules. In simple terms, it’s like picking a class rep in school. You trust them to speak for you. In DPoS, you pick a few to manage the blockchain. These chosen ones are validators who get votes from token holders. The more tokens you hold, the more your vote counts, kind of like having a bigger say in what movie your family watches on movie night because you brought the popcorn.
Distinguishing DPoS from Classic PoS Systems
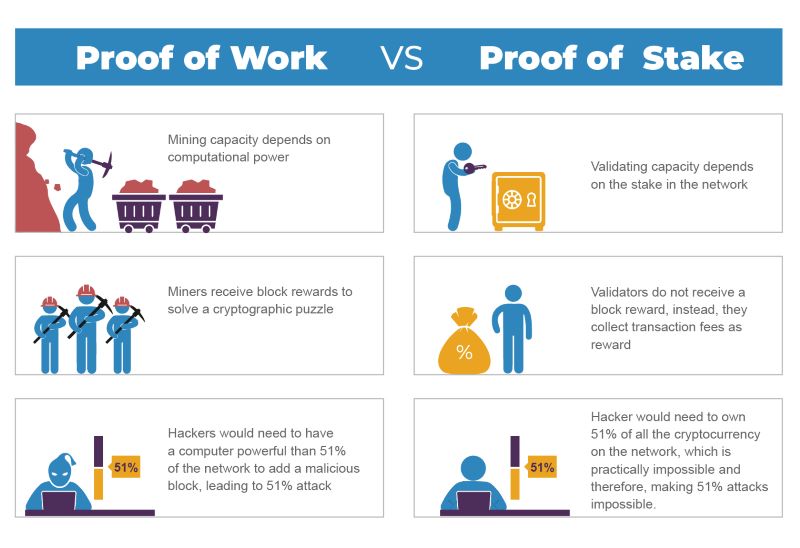
Now, how is DPoS different from regular Proof of Stake, or PoS? Think of PoS as a lottery, but your ticket amount depends on your crypto amount. DPoS is not a game of chance. It uses a voting system to choose validators. This means it’s about who the token holders trust, not just luck.
DPoS is faster than PoS because it has fewer validators. It’s like having a smaller team to make decisions quicker. In PoS, anyone with tokens can help manage the network. It’s more open but usually slower. Also, DPoS makes it cost-effective to run a network. Validators have to do a good job, or they lose their spot. It’s like being on a sports team — you have to play well or you sit on the bench.
People love DPoS because it can handle a lot of transactions without causing a traffic jam. That’s scalability. Security-wise, it’s strong too, because decisions are not in the hands of one but rest with the elected few. This keeps things in check and ensures validators don’t misbehave.
Each time a validator helps in approving transactions, they get rewards. This can be a source of passive income for them. In return, they help keep the network safe. It’s a win-win situation.
In DPoS, those who have tokens but don’t want to vote can give their voting power to someone else. This is called token delegation. It’s like saying, “I trust you, so you can vote for me.” Token holders stay in control by choosing who represents them.
Don’t worry about DPoS being too power-hungry. It’s designed to use less energy compared to Proof of Work networks, that require huge amounts of computer crunching.
Remember though, no system is perfect. DPoS has its own set of challenges and risks. One is that it could become less spread out if only a few validators get all the power. We must always keep an eye on who has how much influence.
In a nutshell, DPoS is about leveraging trust to run a blockchain smoothly. Token holders are like the backbone of the system. They get to vote on who does the hard work. Validators, in exchange for their service and keeping things moving, can earn some rewards. It’s a community-driven way to guard the network and treat it well. So, if you’re into crypto, DPoS is one cool kid on the block worth knowing about.
The Mechanics of DPoS: Efficiency and Scalability
The Role of Witness Nodes in Transaction Validation
Think of witness nodes like the referees in a game. They watch every move, making sure each play follows the rules. In crypto, witness nodes check if transactions are legit. They do this for blockchain to stay safe and sound. These nodes get picked through a vote by everyone who holds tokens. This means they gotta stay honest, or they won’t be picked again. It’s a smart way to keep people in check and the system rolling smooth.
The Impact of Voting Power on Block Production
Now, voting power is a big deal in DPoS. It’s like having a say in who runs a country. The more tokens you own, the more your vote counts. Token holders vote for delegates, and these folks get to forge blocks. What’s forging? It’s when transactions get locked in and become a part of the chain. Delegates have to be good at their job, or they’ll lose their spot. Better delegates mean a faster and stronger blockchain. It’s all about team effort in DPoS, with everyone’s eyes on a better network.
So, remember the next time you’re thinking of Delegated Proof of Stake, it’s all about community power. Folks trust some to look after the rules, and everyone gets a voice through their votes. Efficient, quick, and built on trust – that’s what DPoS brings to the blockchain world.
Stakeholder Governance and Income in DPoS
Navigating the Validator Selection Process
Have you ever asked, “How do folks pick validators in DPoS?” I hear you. In Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), token holders use their coins to vote. They pick a small group out of all the users. These chosen ones are called validators. The voting power rests with how many coins you have. More coins mean more sway in the vote.
Validators play a big part in DPoS. They keep the network safe and running smooth. Think of it as picking the school’s class rep. You want the best, most trusted kid to speak up for you, right? That’s what DPoS does with validators for a blockchain.
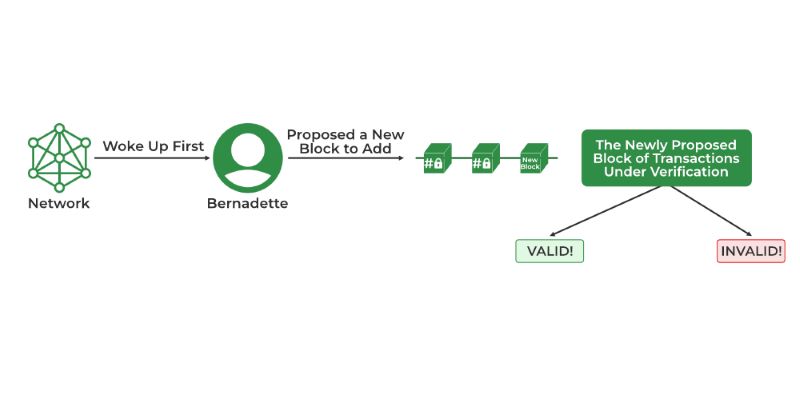
Once picked, validators do two major things. They make new blocks in the chain, which means they handle all the transactions. And they maintain the blockchain’s rules. Breaking a rule can get a validator booted out. Plus, they lose some of their stake. That’s a big no-no, so they tend to play nice.
The process helps the whole system run fast. It also means changes can happen quick if needed. That’s the beauty of DPoS: it’s quick and flexible, making it a top pick for many networks today.
Earning Passive Income through Staking Rewards
Now, here’s the scoop on making money while you chill—staking rewards. By voting for validators, you help secure the network. As a thanks, you get a piece of the pie—rewards. These come from fresh blocks and transactions.
The more you stake, the more rewards you could see. It’s like planting a fruit tree in your yard. It takes some care, but then you get to enjoy the fruits without much hassle. The staking rewards in DPoS work like that. You lock up your coins, the validators work, and you get paid.
Some get worried about locking up coins. But keep this in mind: most times, you can pull out if you need to. So it’s not like your money’s gone for good. With the right know-how, staking gives a decent way to make money.
But watch out! DPoS chains can differ a lot. Each chain has its own rules on how much you get and how long to stake. So it pays to know your stuff or ask someone who does before jumping in. It’s like any investment. You got to understand what you’re putting your coins into.
The need for a big number of coins might seem unfair at first. But think about it: when you got more at stake, you care more about the network’s health. It brings everyone together to look out for the network’s good. And the rewards? They’re just the cherry on top.
In DPoS, token holders, validators, and rewards sync up neatly. This builds a tight ship with folks who are all in it to win it. It’s all about team play, where each player has a vital role. And that, my friend, is what DPoS is all about.
Analyzing DPoS Blockchain Projects and Governance Structures
Case Studies: EOS, Tron, and Lisk Ecosystems
Let’s dive into blockchain worlds where the rules are a bit different. Here, we talk about systems that use Delegated Proof of Stake, or DPoS for short. Think of DPoS as a special way of making all the parts in the system agree without wasting energy or time. We zero in on some big names – EOS, Tron, and Lisk. They are like three different cities, each with its way of keeping the peace and getting things done.
EOS stands out in the crowd. It uses DPoS to run super fast and can handle lots of transactions. The cool thing about EOS is that it lets people build apps that can change the game. These apps work smoothly and can do a lot at once because of DPoS.
Tron is another star. It’s all about sharing media without needing a middle man. Tron’s DPoS means it’s quick and can grow without much trouble. Folks who hold its tokens get to vote on who keeps the system in check.
Now, let’s peek at Lisk. Lisk makes it easy to build blockchain stuff. It’s user-friendly and sticks to DPoS to keep things ticking. In Lisk, holders of the token get a say in who takes care of the ledger.
The Role and Influence of Delegates in Network Participation
In the world of DPoS, we meet a special group: the delegates. Think of them as the chosen ones who get things done in the network. In DPoS systems, being a delegate is a big deal. You get to create new blocks and keep the records straight.
But how does one become a delegate? They are picked by folks who own the crypto. So, if you hold tokens, you’ve got power. Your vote can help decide who becomes a delegate. This way, everyone gets a voice in the network.
What do these delegates do, exactly? They work hard to check and add new blocks to the chain. They keep everything secure and moving like clockwork. If you trust them with your vote, they make sure your transactions go smooth and fast. This makes the system efficient and lets it handle more action.
Token holders, the more you own, the stronger your vote. But even small holders have a key role. They can join forces to shape the network. This is super different from just owning coins and doing nothing. Here, your stake does more than sit – it’s your ticket to influence.
All this voting and selecting makes DPoS stand out from the old-school PoS. It’s made to be more democratic. The system fires on all cylinders, thanks to its delegates. They make sure things get done and that the system can take on more work as it grows. This is what gives DPoS its edge in governance. It’s not just about holding coins; it’s about making your mark.
In this post, we dug into Delegated Proof of Stake, or DPoS. We started by covering the basics of how DPoS works. Then we looked at how it stands apart from other Proof of Stake systems. Our talk showed how witness nodes play a key role and how your votes count in making blocks. We also explored how to pick validators and earn money just by staking.
Then, we checked out real DPoS setups like EOS, Tron, and Lisk. We saw that being a delegate is a big deal and shapes how things run.
To sum up, DPoS is like a more team-driven way of running a blockchain. It’s fast and wide-reaching. Plus, it gives folks like you a say in who’s in charge and even lets you earn a bit for your part. Stay sharp, and keep an eye on how these DPoS projects evolve. They’re a solid slice of the crypto world’s future.
Q&A :
What Is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) in Cryptocurrency?
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus mechanism used by some blockchains to secure their network and verify transactions. It is an evolution of the Proof of Stake (PoS) model and allows stakeholders to vote and elect a limited number of delegates. These elected delegates are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks, which makes the process more democratic and potentially more efficient than traditional Proof of Work (PoW) systems.
How Does Delegated Proof of Stake Differ from Proof of Work?
Delegated Proof of Stake differs significantly from Proof of Work in that it doesn’t require massive amounts of computing power to secure the network. While PoW relies on miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles, which consumes a lot of energy, DPoS instead allows token holders to vote for a small number of nodes (delegates) to validate transactions. This method is intended to be more scalable and energy-efficient.
Why Is Delegated Proof of Stake Considered More Democratic?
Delegated Proof of Stake is considered more democratic because it gives the cryptocurrency community power to vote for their preferred validators. Holders of the cryptocurrency can use their stake to participate in the governance of the blockchain, influencing decisions about the network and electing representatives—much like a representative democracy in governance.
What Are the Advantages of Delegated Proof of Stake?
The primary advantages of Delegated Proof of Stake are increased transaction speeds, reduced energy consumption compared to Proof of Work, and enhanced scalability. These benefits stem from the system’s reliance on a smaller number of validators, which can streamline the consensus process. Furthermore, DPoS systems often include mechanisms for community governance, allowing stakeholders to have a say in important network decisions.
Are There Any Drawbacks to Using DPoS in Cryptocurrency?
While DPoS offers various improvements over other consensus mechanisms, it does have potential drawbacks. One concern is the risk of centralization, as the power to validate transactions might become concentrated in the hands of a few major delegates, potentially compromising the decentralized nature of the blockchain. Another issue is that the requirement to hold tokens to participate might exclude those without sufficient funds to have a meaningful impact on the voting process.
