Blockchain Consensus Algorithms: Unlocking the Secrets to Digital Trust
Let’s dive right in: What is blockchain consensus algorithm? Imagine a world where every digital move counts, a world built on trust not just given, but earned and proven. Consensus algorithms are the core of blockchain technology, the clever tricks that let countless computers agree on who owns what, without ever meeting face to face.
They’re the unsung heroes that keep everything from your favorite cryptos to entire blockchain networks honest and on track. In this post, I’ll unpack these digital magicians, showing you not just what makes them tick, but how they power the trust we place in the next-gen internet—blockchain. Buckle up; we’re about to explore the brilliant guts of these systems!
Understanding Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
The Role of Consensus in Decentralized Ledger Technology
In a world where no single person is in charge, how do we trust what happens online? This is where blockchain consensus mechanisms step in. They make sure everyone agrees with the list of records, without needing a boss. Just like a game where everyone plays by the rules, blockchain ensures all players agree on the score.
A blockchain is a long list of records tied together. It’s safe from tinkering because changing one record would mess up the rest. Consensus protocols in cryptocurrency help keep this ledger in check. They’re like referees in this game, ensuring players don’t cheat and records stay true.
Comparing Consensus Protocols in Cryptocurrency
Now let’s chat about proof of work vs proof of stake – two big ways to reach consensus in crypto.
Proof of work is like a race where miners solve puzzles to add new blocks to the chain. The first to solve the puzzle gets new coins. But this race munches a lot of energy, sparking talks on its hefty power bill.
Proof of stake, on the other hand, picks the creator of a new block based on their wealth in the network or “stake.” It’s like picking a class monitor based on who has the most gold stars. It uses way less energy and is like a green badge in the crypto world. Ethereum switch to proof of stake is like a popular kid getting that green badge, showing others it’s cool.
Some folks might ask, “How proof of work operates?” Imagine a ton of computers racing to solve math problems. The winner adds a new block and shouts, “Bingo!” earning some digital cash.
On energy stuff, mining gobbles up loads of juice – think of all the computers running day and night. But proof of stake wants to change that. It looks at who’s got skin in the game, not who’s got the most muscle.
When you hear “byzantine fault tolerance explained,” think of it as a trust test for computers. It makes sure all computers, or “nodes,” act honest even if some play dirty.
For digital trust, we need rules to prevent foul play. Sybil attack prevention stops one player from using many masks to sway the game. And a 51 percent attack is when a player gets over half the power and can twist the game. We keep watch to stop these nasty moves.
In this tech jungle, smart contracts are our tools. They’re like robot helpers that do tasks when certain things happen, making sure deals stick.
Lastly, talking about trust in distributed systems, it’s all about setting up a fair game where no one cheats. A decentralized consensus model is the key, letting every player have a say and keeping the record book open and honest. The beauty of blockchain is that everyone has the same notes, and if someone tries to cheat, it sticks out like a sore thumb.
The Mechanics of Leading Consensus Algorithms
How Proof of Work and Proof of Stake Operate
Let’s dive into blockchain consensus mechanisms, but we’ll keep it simple. Think of it as how these networks reach an “agreement.” First off, we have Proof of Work (PoW). It’s the muscle behind Bitcoin. Here, miners solve complex puzzles using powerful computers. When they solve it, they get to add a new “block” of transactions to the blockchain. This is how proof of work operates. But it’s not just about creating blocks; they also make sure all transactions are legit. This prevents double-spending, which is someone trying to spend the same money twice.
Now, PoW’s big thing is energy use. You’ve heard how it uses as much power as whole countries, right? This energy consumption in mining is a hot topic. That’s where Proof of Stake (PoS) comes in – it’s like the thoughtful cousin of PoW. Instead of puzzle-solving, you can create new blocks if you hold some coins and are chosen by the system. It uses a lot less electricity.
So why do we care about how these work? Well, each method is key in keeping the blockchain secure and trusted. This is what we call blockchain security through consensus.
Byzantine Fault Tolerance and Alternative Consensus Models
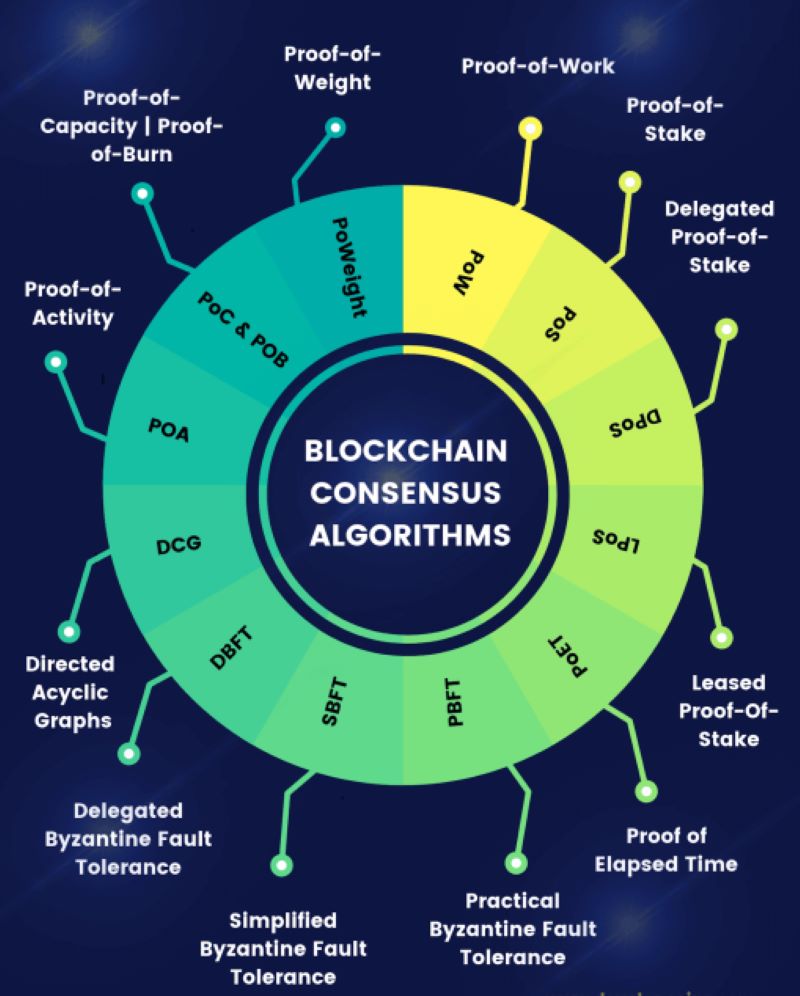
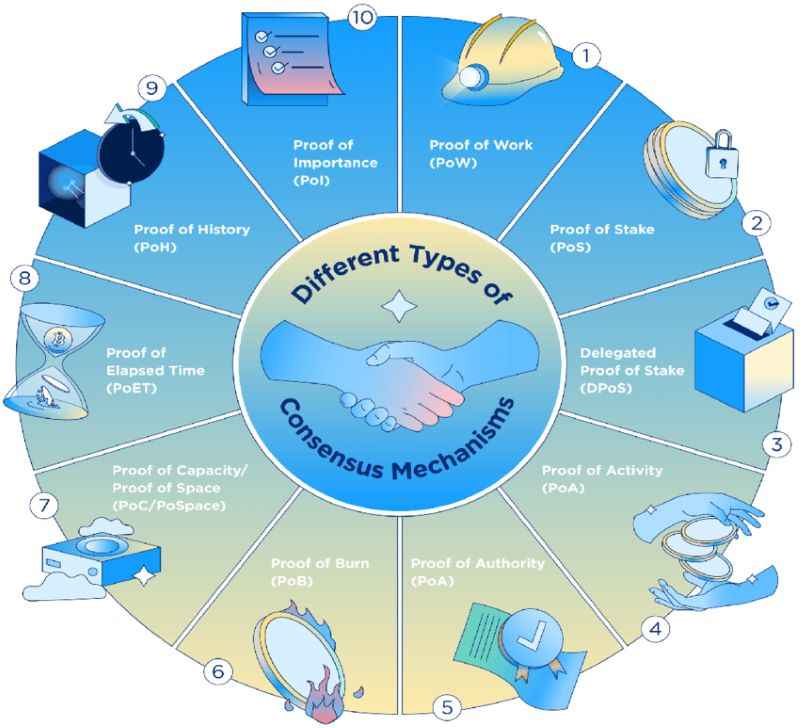
Now, there’s more than PoW and PoS out there. One shining star is Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT). Byzantine fault tolerance explained simply, it’s a way for a system to still work even if some parts fail or act sneaky. Imagine a group trying to agree on something when a couple of folks are lying. Tough, right? With BFT, even with some shady nodes, the network can still reach a consensus and keep the ledger correct.
There are spins on PoS too, like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), where people vote on who gets to create the new blocks. Then you have Proof of Authority (PoA), which has a few chosen validators based on reputation and identity. These models aim for the same goal: ledger consistency in blockchain – ensuring everyone agrees on what the ledger says.
Think about nodes like town folks who must agree on where to put a road. They must all say “Yes, that’s the right spot.” That’s decentralized consensus model in action – no boss, just the group decision.
These ideas help us solve real tech puzzles. Like, how do we make transactions zip faster (scalability issues in blockchain) or stop fraudsters (sybil attack prevention)? How do we keep the network just and fair (blockchain governance)? As we get smarter and the tech does too, these consensus protocols in cryptocurrency keep evolving.
This whole discussion matters because at heart, blockchain offers a fresh way to do trust. Trust in digital systems is tough. But with these algorithms at work, you can feel safe knowing that your digital money, contracts, and data are being treated right. They are the secret sauce to digital trust and the reason we can count on blockchains to handle our most valuable assets with care.
The Implications of Consensus Design
Impact on Energy Consumption and Network Scalability
Blockchain consensus mechanisms are the heart of trust in digital systems. They let a group of computers agree on something, like a transaction, without needing one boss. Proof of Work (PoW) is one heavily used method. Many people know about how proof of work operates; it lets one machine confirm a bunch of transactions by solving hard puzzles. The machine that solves the puzzle gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. This is how Bitcoin works, for example.
However, energy consumption in mining for PoW is high. Each machine in the network tries to solve puzzles fast. They use lots of power trying to win the new block reward. This has made people watch the energy use of networks like Bitcoin.
On the other hand, Proof of Stake (PoS) and other methods like Proof of Authority are rising. They promise the same safety but use much less power. Ethereum’s switch to proof of stake is a big deal here. It’s moving from PoW to PoS to cut down on energy use. With PoS, people lock up some of their own cryptocurrency. If they prove they own this “stake,” they can help validate new transactions. It uses way less energy and can help the network handle more transactions.
Scalability issues in blockchain are real. As more people use a network, it can get slow and costly. PoW is not great at scaling. PoS and other methods aim to fix this. They want to let blockchains grow without getting bogged down.
Security Considerations: From Node Validation to Preventing Attacks
Blockchain security through consensus is key. The network has to check if all the nodes, or computers, play by the rules. This node validation process helps keep the network honest. If a node tries something fishy, like double-spending, other nodes can spot it. They won’t let the bad transaction into the blockchain.
What about bad actors? Attacks like the Sybil attack or the 51 percent attack can mess things up. In a Sybil attack, someone makes a lot of fake identities to gain control. In a 51 percent attack, a group might control more than half the network’s power. They can then approve fake transactions. Consensus methods help stop these kinds of attacks by making rules really tough to break.
We also care about the distributed network agreement. It’s what lets a blockchain be a trusted ledger. Without it, we can’t be sure that what the blockchain says is true. Nakamoto consensus, used in Bitcoin, has been working well for this. It combines PoW with a rule that the longest chain of blocks is always the true one.
In smart contracts and other blockchain apps, trust is built into the code. But even then, the underlying consensus method must be strong. It ensures the transactions that trigger the contracts are legit.
Ledger consistency in blockchain depends on all these things. We need honest nodes and good rules to keep our digital records straight. With technology moving fast, we keep finding new ways to make sure every transaction is final and true. This keeps our digital world running smoothly.
The Future of Blockchain Consensus
The Transition of Ethereum and Innovation in Consensus Protocols
We are seeing a game-changer in how blockchains reach agreement. Ethereum, a giant in the field, is moving to Proof of Stake (PoS). This is big news. But what exactly is happening here?
In simple terms, Ethereum is shifting gears. It’s moving from a power-hungry to an energy-saving way of running the show. When we talk about blockchain consensus mechanisms, think of them as rules of a game. These rules decide who gets to add the next page to our digital ledger book.
Before, Ethereum used Proof of Work (PoW), where miners solved puzzles to write new transactions. With PoS, it’s like a raffle. The more digital currency you hold, the better your odds of being picked to write the next page. It’s like holding lots of raffle tickets in a draw.
This switch is a big deal. It’s not just a new way to validate transactions. It’s a leap towards cutting down electricity use. We want our digital worlds to be clean, right? Green is the future! And with Ethereum taking the lead, others are sure to follow.
We’re not only saving energy. We’re revving up for more creativity in reaching consensus. Now, tech wizards can invent fresh protocols without always fretting over energy bills. New ideas will bubble up, making blockchains even better and faster.
Other cool inventions are joining the party too. Like Proof of Authority where trusted users get the say. Or Delegated Proof of Stake which is like having representatives in the blockchain world. It’s an exciting time as these new ideas can help make every vote, every transaction, and our trust stronger in this online space.
Governance and the Evolution of Blockchain Consensus Models
Now, let’s chat governance. Fancy word, but it’s really about making decisions together. In the blockchain land, governance shapes how groups agree on changes or rules.
Blockchain governance is, well, unique. You’ve got all these far-out ways to deal out power like stakeholder voting systems. They’re ways to let folks who have a stake in the blockchain help make the big calls. It’s democracy, but run on technology. Talk about power distribution!
As we refine consensus models, governance evolves too. It has to, right? The blockchain world doesn’t stand still. We’re always looking to strike that sweet spot between people having their say and keeping our systems running smooth.
Hard forks, where a blockchain splits in two, show how crucial governance is. They can shake things up, causing storms in our digital community. But, by getting governance right, we can navigate those storms together.
In each step we take, whether it’s adding smart contracts that act like sealed deals, or stopping bad players with new tech smarts, governance is the backbone. It’s the promise that keeps our digital trust alive.
Ledger consistency, security, and trust are what this whole consensus journey is about. As we zip into the future, these advances in blockchain consensus ensure our digital world stays reliable, efficient, and most importantly, trustworthy. This is just the beginning, and I can’t wait to see where we’re headed next.
In this post, we dove deep into blockchain consensus mechanisms. We looked at their vital role in decentralized ledger technology and compared popular protocols in cryptocurrency. We unwrapped the mechanics of Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, along with other models like Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
We also tackled how consensus design affects energy use and a network’s ability to grow. Security is key, so we discussed how these systems defend against attacks. Finally, we looked ahead at what’s coming for blockchain consensus, from Ethereum’s big move to the future of governance.
To wrap it up, understanding these mechanisms means you can grasp how blockchains stay honest and grow. It’s complex but fascinating, shaping the backbone of crypto’s world. Stick around to see how this tech will evolve. It’s changing fast, and there’s more to come. Keep learning and stay smart!
Q&A :
What Is a Blockchain Consensus Algorithm?
A blockchain consensus algorithm is a protocol used within a blockchain network to achieve agreement on the state of the ledger among all participating nodes. It ensures that all transactions are verified and accepted by the majority of the system participants, thus maintaining the integrity and consistency of the blockchain.
How Do Consensus Algorithms Ensure Transactions Are Valid?
Consensus algorithms employ various mechanisms to validate and agree upon transactions. They prevent double spending and ensure that all copies of the distributed ledger are synchronized across the network. Techniques such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) are commonly used to achieve this.
What Are the Different Types of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms?
The most well-known consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT). Each mechanism has its unique approach to achieving consensus and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the blockchain’s performance, security, and governance.
Why Is a Consensus Algorithm Important to Blockchain Technology?
Consensus algorithms are crucial because they provide a trustworthy and fault-tolerant method to establish consensus in a decentralized environment, without needing a central authority. This is key to the nature of blockchain technology, which operates on a peer-to-peer network and demands high security and fidelity in transaction processing.
How Do Consensus Algorithms Affect the Scalability and Security of a Blockchain?
Consensus algorithms play a significant role in determining the scalability and security of a blockchain. Some algorithms, like PoW, are very secure but can lead to slower transaction processing times. Others, like PoS, offer faster transactions but require a different approach to network security. Selecting the right algorithm can help balance these aspects to suit the blockchain’s purpose.